Photoacoustic NDIR Sensing
Photoacoustic NDIR sensing combines the strengths of both photoacoustic spectroscopy and NDIR methods.
Photoacoustic NDIR Sensing
Photoacoustic Non-Dispersive Infrared (NDIR) sensing is a hybrid technology that combines the principles of photoacoustic spectroscopy and NDIR techniques to detect and measure the concentration of gases. This technology enhances traditional NDIR methods by incorporating photoacoustic detection mechanisms, improving sensitivity for gas detection.
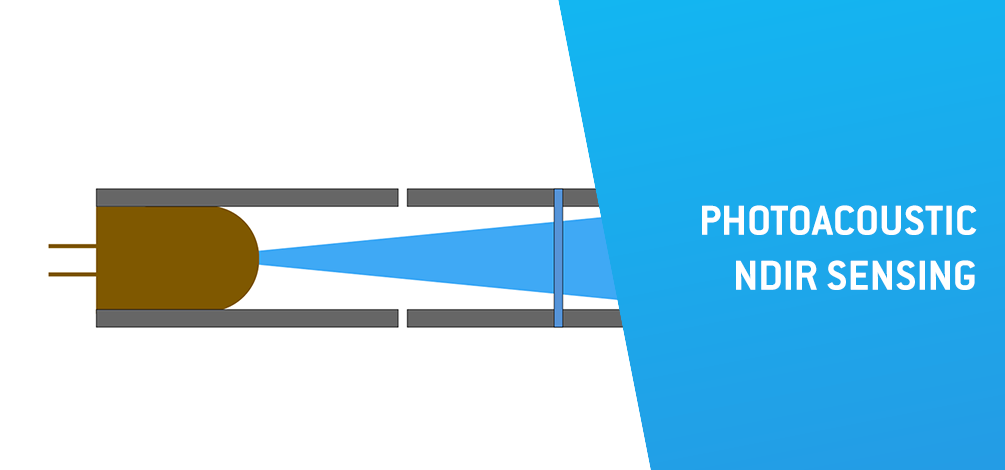
The photoacoustic NDIR sensing technique leverages a unique physical phenomenon. In Figure 1 we can observe the sensor setup and notice the fact that the photoacoustic NDIR sensor has an infrared source which is modulate at a specific frequency.
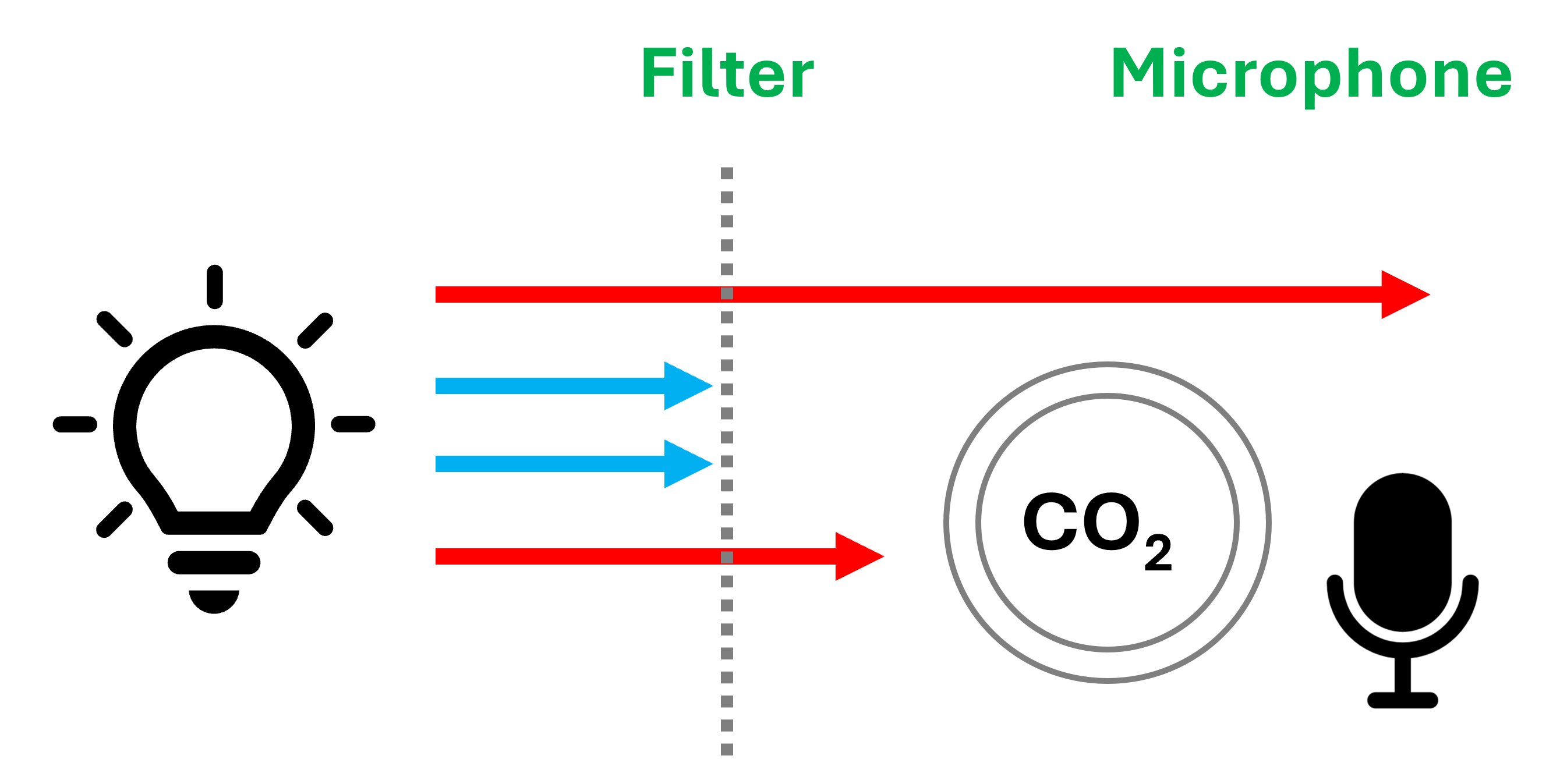
The modulated infrared radiation passes through an optical filter, ensuring only the wavelengths absorbed by the target gas reach the gas sample (ex. 4,2 µm for CO2).
When pulsing the infrared emitter, the CO2 molecules absorb the radiation periodically. This causes molecular vibration resulting in a pressure wave inside the measurement chamber. For instance, the higher the CO2 concentration, the more radiation is absorbed, and thus the greater the amplitude of this acoustic wave becomes.
A highly sensitive microphone inside the gas chamber measures the acoustic waves, from which the gas concentration can then be calculated.
The signal processing capability allows the sensor to maintain high accuracy even in challenging environments with potential interferences or background noise.
Why using Photoacoustic NDIR
The main advantage of photoacoustic NDIR sensing comparing to other technologies is the high sensitivity, detecting very low concentrations of gases, making the technology suitable for trace gas analysis.
Unlike transmissive NDIR sensors, for example, which measure the amount of light transmitted through a gas sample, photoacoustic NDIR sensors detect the energy absorbed by CO2 molecules.
This fundamental difference in detection offers other types of benefits, such as mechanical robustness and a significant size reduction.
Tailored Detection for Multiple Applications
The technology can be tailored to detect specific gases by only choosing appropriate optical filters and modulation frequencies. Photoacoustic NDIR sensors are compact and suitable for various applications.
Currently, these sensors are used in:
- Environmental Monitoring: measurement of atmospheric gases like CO2 (carbon dioxide), CH4 (methane), and NOx (nitrogen oxide) to monitor air quality and greenhouse gas concentrations.
- Industrial Safety: detection of hazardous gases in industrial environments to ensure worker safety.
- Medical Diagnostics: non-invasive monitoring of gases like CO (carbon monoxide) and CO2 in breath analysis.
- Automotive Emissions: monitoring exhaust gases to ensure compliance with emission standards.
Although CO2 detection is its primary application, the photoacoustic NDIR principle can be adapted to detect other gases by selecting appropriate optical filters and modulation frequencies.
Such versatility makes photoacoustic NDIR technology a promising platform for multi-gas analysis systems in various fields.
Innovating with Photoacoustic NDIR
Photoacoustic NDIR sensing combines the strengths of both photoacoustic spectroscopy and NDIR methods, resulting in a powerful tool for accurate and sensitive gas detection across various fields.
Tekon Electronics integrates photoacoustic NDIR sensors to monitor CO2 levels in the DUOS inAir and DUOS inCO2 transmitters. These solutions are important, as CO2 is a key indicator to monitor the IAQ (Indoor Air Quality), and high levels affect cognitive performance and well-being.
Tekon Electronics continues to reaffirm its contribution to innovation, providing competitive and distinctive IoT solutions.
Join us on this journey towards a smarter and more connected future!
Sensirio. What types of NDIR sensors exist and how do they work?. https://sensirion.com/media/documents/9E7DA521/627C2C8D/CD_IN_SCDxx_Transmissive_and_photoacoustic_NDIR_sensing_D1.pdf
AirGradient. Low Cost CO2 Sensors Comparison: Photo-Acoustic vs NDIR. https://www.airgradient.com/blog/co2-sensors-photo-acoustic-vs-ndir/
SparkFun Electronics. Carbon Dioxide Sensing: PAS vs NDIR vs TVOC. https://www.sparkfun.com/news/8952
Sentera Controls. What are the advantages of photoacoustic NDIR CO2 sensors? https://www.sentera.eu/en/faq/a/what-are-the-advantages-of-photoacoustic-ndir-co2-sensors/1074
S. Palzer. Photoacoustic-Based Gas Sensing: A Review. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7248969/
D. Popa and Florin Udrea. Towards Integrated Mid-Infrared Gas Sensors. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6539445/